YOUR POSITION: HOME > Information
Edit:Zongxiang Heavy Industry--Ethan Date:2023-04-13 14:18:26
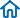
A rail turnout, also known as a railroad switch or points, is a mechanical device used in railways to enable trains to be directed from one track to another. It consists of movable rails that connect to two or more tracks, allowing trains to switch between them. Rail turnouts are essential components of any railway system as they allow trains to navigate around obstacles, pass each other on single-track lines, and access sidings and terminals.
The primary function of a rail turnout is to provide a safe and efficient means for trains to change tracks. This is achieved by using movable rails that can be adjusted to direct a train onto a different track. The basic design of a rail turnout consists of a pair of stock rails that run parallel to each other and a set of movable rails, which are known as switch rails. The switch rails are attached to the stock rails with a mechanism that allows them to be rotated to one side or the other. When the switch rails are in their normal position, they are aligned with the stock rails, allowing the train to continue straight ahead. However, when the switch rails are moved, they create a diverging route, which the train can follow onto a different track.
There are several different types of rail turnouts, each designed for specific purposes. One common type is the simple turnout, which consists of two switch rails that are connected to a common throw bar. When the throw bar is moved, the switch rails rotate in opposite directions, allowing the train to follow one of two diverging routes. Another type of turnout is the double slip switch, which allows a train to move onto one of four different tracks. This is achieved by using two pairs of switch rails that are connected together to create a diamond-shaped junction. As the train approaches the junction, the switch rails are rotated to direct it onto the appropriate track.
The function of a rail turnout goes beyond just switching tracks. They also play a crucial role in ensuring the safety and efficiency of railway operations. Turnouts must be designed and maintained to meet strict safety standards to prevent derailments and other accidents. This involves regular inspection and maintenance of the turnout components, including the switch rails, stock rails, and the mechanism that controls them.
Another critical function of rail turnouts is to manage traffic flow on the railway system. Turnouts allow trains to move around obstacles, such as other trains, and to access sidings and terminals for loading and unloading cargo. By enabling trains to move onto different tracks, turnouts allow for more efficient use of the railway system, reducing congestion and delays.
In addition to their primary functions, rail turnouts also have a significant impact on the speed and comfort of train travel. When a train passes over a turnout, there is a slight bump caused by the gap between the stock rails and the switch rails. This can be minimized by using longer switch rails or by filling the gap with a resilient material. The smooth operation of turnouts is essential for maintaining passenger comfort and preventing damage to the rolling stock.
Finally, rail turnouts also have a significant economic impact. They allow trains to access different parts of the railway network, which can improve the efficiency of freight transportation and reduce costs. Turnouts also enable the construction of new railways and extensions to existing lines, opening up new markets and opportunities for economic growth.
In conclusion, the function of rail turnouts is multifaceted, serving to provide a safe and efficient means for trains to change tracks, manage traffic flow on the railway system, and improve the speed and comfort of train travel. Their impact extends beyond the railway industry, contributing to economic growth and development. As such, turnouts are essential components of any railway system and must be designed and maintained to meet the highest standards of safety and efficiency.
Online Chat


To top